Parts of the Triceps Brachii Muscle
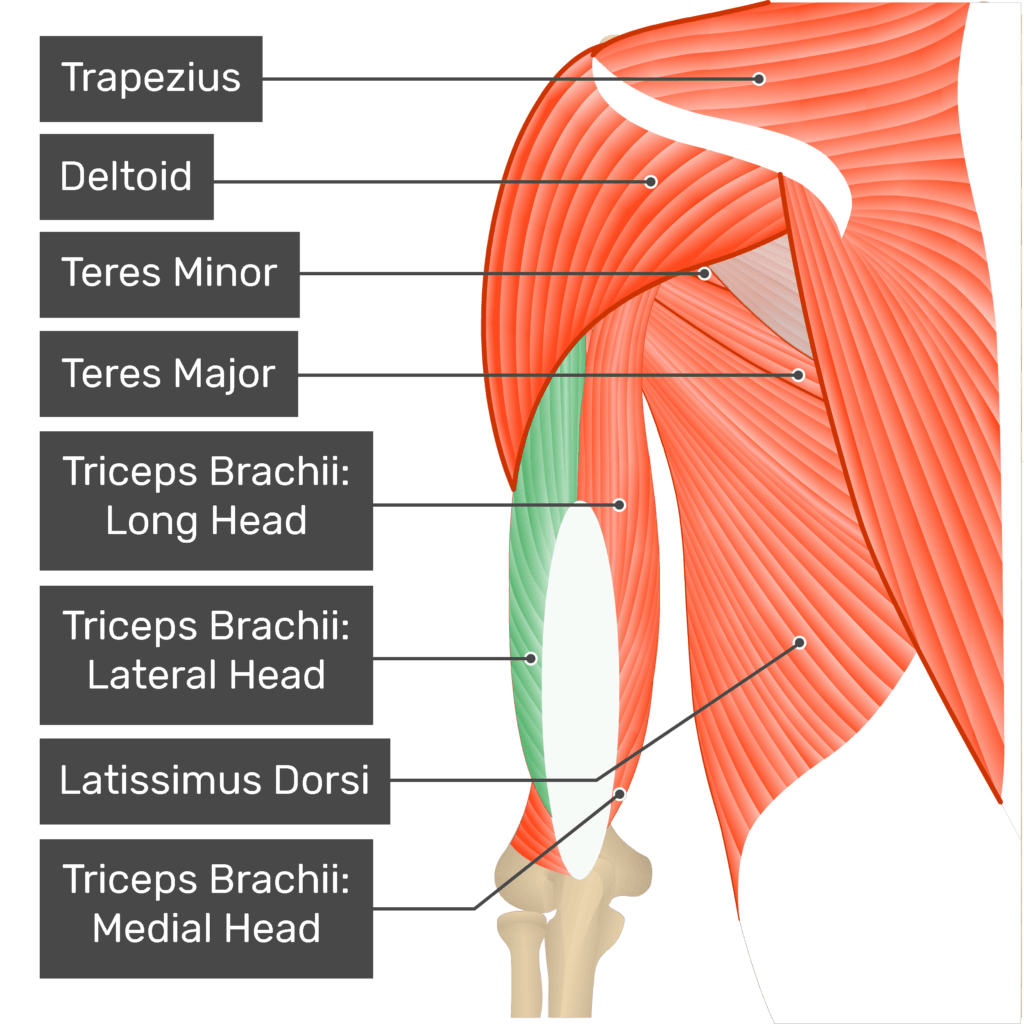
Parts of the Triceps Brachii Muscle
The triceps brachii is one of the most important muscles in the human body, especially when it comes to arm movement and strength. This large muscle spans the back of the upper arm and plays a critical role in extending the forearm. It is composed of three distinct parts or heads: the long head, the lateral head, and the medial head. Each of these heads originates from different points on the body and contributes uniquely to the overall function of the triceps brachii.
Understanding the anatomy of the triceps brachii is essential for athletes, fitness enthusiasts, and anyone interested in improving their upper body strength. The muscle's structure allows it to perform its primary function—elbow extension—with precision and power. Additionally, the triceps brachii helps stabilize the shoulder joint, making it indispensable for activities that require both strength and coordination. Let’s delve deeper into each part of this remarkable muscle.
Long Head of Triceps Brachii
The long head of the triceps brachii is the largest and deepest of the three heads. It originates from the infraglenoid tubercle of the scapula, which is located just below the shoulder socket. This unique origin point makes the long head the only part of the triceps brachii that crosses two joints: the shoulder and the elbow. As a result, the long head not only assists in elbow extension but also provides stability to the shoulder joint.
This dual functionality makes the long head particularly important for movements that involve overhead lifting or pushing, such as military presses or bench presses. When you engage in these types of exercises, the long head works in tandem with other muscles to ensure smooth and controlled motion. Its position deep within the muscle also means that targeting the long head specifically can be challenging, requiring exercises that emphasize shoulder stabilization alongside elbow extension.
Importance of the Long Head
The long head is often referred to as the "stabilizer" of the triceps brachii due to its role in maintaining shoulder joint integrity. Without the long head, the shoulder would lack the necessary support during dynamic movements, increasing the risk of injury. Athletes who frequently perform overhead movements, such as swimmers, tennis players, and weightlifters, rely heavily on the long head to prevent dislocations and maintain proper alignment.
In addition to its stabilizing function, the long head contributes significantly to the overall size and shape of the triceps. Its length and depth give the muscle its characteristic bulk, which is highly sought after by bodybuilders and fitness enthusiasts. To maximize the development of the long head, exercises that incorporate shoulder involvement, such as close-grip pull-ups or overhead extensions, are highly recommended.
Targeting the Long Head
To effectively target the long head, it is crucial to choose exercises that place emphasis on both elbow extension and shoulder stabilization. Here are some examples:
- Close-Grip Pull-Ups: This exercise engages the long head by requiring the shoulders to remain stable while the elbows extend.
- Overhead Dumbbell Extensions: By holding the dumbbell above your head, you activate the long head as it works to stabilize the shoulder joint while extending the elbow.
- Cable Pushdowns with Rope: Using a rope attachment allows for a full range of motion, ensuring that the long head is fully engaged throughout the movement.
Lateral Head of Triceps Brachii
The lateral head of the triceps brachii is the most superficial of the three heads, meaning it lies closest to the skin. It originates from the posterior surface of the humerus, above the radial groove, and is primarily responsible for the horseshoe shape that many people associate with well-developed triceps. The lateral head is often considered the "showpiece" of the triceps because it is the most visible and aesthetically prominent.
Despite its superficial location, the lateral head plays a vital role in the functional strength of the triceps brachii. It works in conjunction with the other heads to facilitate powerful elbow extensions, making it an essential component of any strength-training program. Exercises that focus on the lateral head can help improve overall arm definition and enhance performance in activities that require explosive power.
Role in Elbow Extension
The lateral head is particularly active during movements that require maximal elbow extension, such as push-ups, dips, and bench presses. Its position on the outer side of the arm allows it to generate significant force, contributing to the triceps' ability to lift heavy loads. Athletes who prioritize developing the lateral head often notice improvements in their ability to perform these exercises with greater efficiency and power.
Moreover, the lateral head is involved in fine motor control, aiding in tasks that require precision and accuracy. For example, when writing or typing, the lateral head helps maintain the stability of the forearm, allowing for smooth and controlled movements. This versatility makes the lateral head an indispensable part of daily life, whether you're engaging in physical activity or performing routine tasks.
Exercises for the Lateral Head
To target the lateral head effectively, it is important to focus on exercises that emphasize elbow extension with minimal shoulder involvement. Here are some practical suggestions:
- Dips: This bodyweight exercise isolates the triceps, with the lateral head being particularly active due to its position on the outer arm.
- Barbell Close-Grip Bench Press: By narrowing your grip, you shift the focus away from the chest and onto the triceps, specifically targeting the lateral head.
- Tricep Kickbacks: Using dumbbells, this exercise ensures that the elbow remains stationary while the arm extends, maximizing engagement of the lateral head.
Medial Head of Triceps Brachii
The medial head of the triceps brachii is the smallest and least visible of the three heads. It originates from the posterior surface of the humerus, below the radial groove, and runs parallel to the lateral head. Although it may not be as prominent as the other heads, the medial head plays a crucial role in the overall strength and endurance of the triceps brachii. Its primary function is to assist in elbow extension, providing additional power and stability during repetitive or sustained movements.
The medial head is often referred to as the "workhorse" of the triceps because it is highly resistant to fatigue. This characteristic makes it particularly important for endurance-based activities, such as rowing, cycling, or swimming. By supporting the other heads during prolonged use, the medial head ensures that the triceps brachii can continue functioning effectively even under demanding conditions.
Contribution to Strength and Endurance
While the medial head may not contribute significantly to the aesthetic appeal of the triceps, its role in enhancing functional strength cannot be overstated. It works tirelessly in the background, providing the necessary support for the long and lateral heads to perform at their best. This synergy between the three heads is what makes the triceps brachii such a powerful and versatile muscle group.
In addition to its endurance capabilities, the medial head also aids in fine motor control, much like the lateral head. However, its contribution is more subtle, focusing on maintaining stability rather than generating force. This dual functionality makes the medial head an essential component of both strength and precision-based movements.
Developing the Medial Head
To develop the medial head, it is important to incorporate exercises that emphasize high repetitions and sustained effort. Here are some effective options:
- High-Rep Tricep Pushdowns: Performing pushdowns with lighter weights and higher repetitions can help build endurance in the medial head.
- Skull Crushers: This exercise targets all three heads of the triceps but places particular emphasis on the medial head due to its sustained contraction.
- Bodyweight Tricep Dips (with added resistance): Adding resistance bands or wearing a weighted vest can increase the demand on the medial head, helping to build both strength and endurance.
Function of the Triceps Brachii
The primary function of the triceps brachii is elbow extension, which is the straightening of the arm at the elbow joint. This movement is fundamental to countless daily activities, from opening doors to lifting objects. The triceps brachii achieves this through the coordinated action of its three heads, each contributing to the overall power and precision of the movement.
In addition to elbow extension, the triceps brachii also plays a key role in stabilizing the shoulder joint. The long head, in particular, provides critical support during overhead movements, ensuring that the shoulder remains aligned and secure. This dual functionality makes the triceps brachii an indispensable muscle group for both strength and mobility.
Practical Applications
The importance of the triceps brachii extends beyond the gym, impacting nearly every aspect of daily life. Whether you're carrying groceries, typing on a keyboard, or playing sports, the triceps brachii is actively engaged. Strengthening this muscle group can lead to improvements in both physical performance and quality of life.
For athletes, developing the triceps brachii can enhance performance in a variety of sports. For example, swimmers rely heavily on the triceps for propulsion through the water, while basketball players use them to shoot accurately and consistently. Even non-athletes can benefit from stronger triceps, as improved arm strength can make everyday tasks easier and reduce the risk of injury.
Detailed Checklist for Triceps Development
To ensure optimal development of the triceps brachii, follow this detailed checklist:
- Identify Your Goals: Determine whether you want to focus on strength, endurance, or aesthetics. This will help guide your exercise selection and training regimen.
- Target All Three Heads: Incorporate exercises that specifically target the long, lateral, and medial heads. Use a combination of compound movements (e.g., dips, bench press) and isolation exercises (e.g., pushdowns, kickbacks).
- Vary Your Rep Ranges: Alternate between high-rep, low-weight exercises for endurance and low-rep, high-weight exercises for strength. This approach ensures balanced development of all three heads.
- Emphasize Proper Form: Focus on maintaining correct form during each exercise to avoid injury and maximize effectiveness. Engage your core and keep your movements controlled and deliberate.
- Incorporate Progressive Overload: Gradually increase the weight or resistance over time to challenge your muscles and encourage growth. This principle is essential for achieving long-term progress.
- Allow for Adequate Recovery: Ensure that you give your muscles sufficient time to rest and recover between workouts. Overtraining can lead to fatigue and increased risk of injury.
- Monitor Your Progress: Keep track of your workouts, including the exercises performed, weights used, and number of repetitions. This will help you identify areas for improvement and celebrate your successes.
By following this checklist, you can develop a comprehensive and effective training program tailored to your specific needs and goals. Remember that consistency and dedication are key to achieving lasting results. With the right approach, you can unlock the full potential of your triceps brachii and enjoy the benefits of stronger, more functional arms.
Deja una respuesta