Parts of Car AC
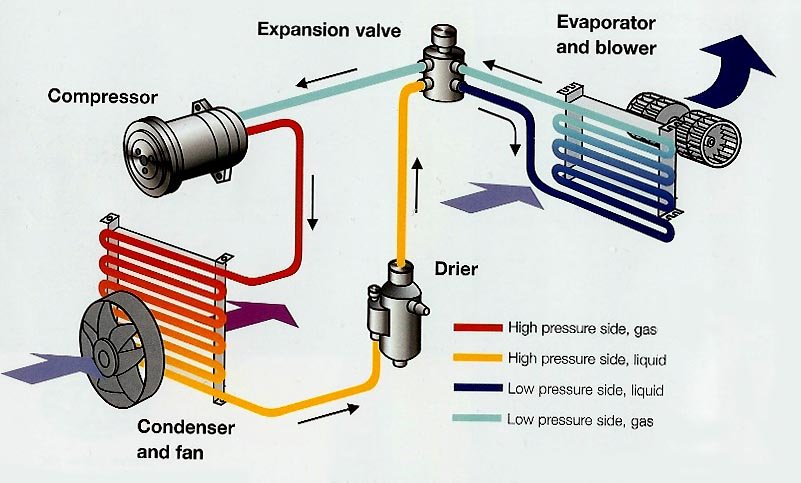
Parts of Car AC
The air conditioning system in your car is a marvel of engineering, designed to keep you cool and comfortable during those sweltering summer months. However, it's not just one single component that makes this possible; rather, it's an intricate network of parts working together seamlessly. Understanding these parts of car AC can help you maintain your vehicle's cooling system more effectively and troubleshoot issues when they arise. In this section, we will delve into the compressor, which plays a pivotal role in the functioning of the entire system.
Compressor
The compressor is often referred to as the heart of the car's air conditioning system. Its primary function is to pressurize the refrigerant, transforming it from a low-pressure gas into a high-pressure gas. This process is crucial because it initiates the heat exchange cycle that ultimately cools the air inside your car. The compressor is powered by the engine via a belt, and it operates only when the air conditioning system is turned on.
To understand how the compressor works, imagine it as a pump that moves refrigerant through the system. When the compressor engages, it draws in the refrigerant in its gaseous state and compresses it, increasing both its pressure and temperature. This high-pressure, high-temperature gas is then sent to the condenser for further processing. Without the compressor, the refrigerant would remain in its low-pressure state, making the cooling process impossible.
Maintaining the compressor is essential for the longevity of your car's air conditioning system. Regular inspections can help identify potential issues such as leaks or wear and tear. If the compressor fails, it can lead to a complete breakdown of the system, leaving you without any cooling capabilities. It's also worth noting that the compressor requires lubrication to function properly, so ensuring there's enough oil in the system is critical.
Common Issues with the Compressor
One common issue with the compressor is a lack of proper lubrication, which can cause excessive wear and eventual failure. Another problem could be electrical malfunctions, where the compressor clutch fails to engage due to a faulty relay or wiring issue. Additionally, physical damage from debris or accidents can compromise the compressor's ability to function correctly. Addressing these issues promptly can save you from costly repairs down the line.
Condenser
Next in line is the condenser, another vital component of the car's air conditioning system. Located at the front of the vehicle, usually near the radiator, the condenser serves as a heat exchanger. Its job is to dissipate the heat absorbed by the refrigerant from the cabin and release it into the outside air. This process transforms the refrigerant from a high-pressure gas back into a liquid state, preparing it for the next stage of the cooling cycle.
The condenser resembles a radiator in appearance, consisting of a series of tubes and fins that maximize surface area for efficient heat transfer. As the high-pressure gas enters the condenser, it encounters cooler air flowing through the fins, facilitated by the car's forward motion or the cooling fan. This interaction causes the refrigerant to lose heat and condense into a liquid form.
Proper maintenance of the condenser is crucial for optimal performance. Over time, dirt, dust, and debris can accumulate on the fins, obstructing airflow and reducing the condenser's efficiency. Regular cleaning with compressed air or a mild detergent solution can help prevent such blockages. Furthermore, checking for leaks is important, as even small leaks can significantly impact the system's ability to cool the cabin effectively.
Importance of Proper Airflow
The effectiveness of the condenser heavily relies on adequate airflow. Ensuring that the cooling fans are functioning correctly and that there are no obstructions around the condenser can make a noticeable difference in the system's performance. Drivers in urban areas, where traffic congestion is common, may find that their air conditioning systems work less efficiently due to reduced airflow. Installing auxiliary fans or using higher-quality condensers can mitigate this issue.
Evaporator
The evaporator is the component responsible for absorbing heat from the cabin air and cooling it before it is circulated back into the passenger compartment. Positioned inside the dashboard, the evaporator acts as another heat exchanger but operates in reverse compared to the condenser. Here, the refrigerant absorbs heat from the warm air passing over its surface, causing it to evaporate into a gas.
As the refrigerant flows through the evaporator, it absorbs heat from the air blown across it by the blower fan. This process lowers the temperature of the air, which is then directed into the cabin, providing the desired cooling effect. Simultaneously, moisture in the air condenses on the cold evaporator surfaces, which is why you might notice water dripping from beneath your car during humid conditions.
Maintaining the evaporator involves keeping it clean and free from contaminants. Dust, pollen, and other particles can accumulate on the evaporator's fins, reducing its ability to absorb heat efficiently. Periodic cleaning with specialized products designed for automotive evaporators can help restore performance. Additionally, addressing any leaks promptly is essential, as they can lead to refrigerant loss and diminished cooling capacity.
Preventing Mold and Mildew
Since the evaporator deals with moisture, it can become a breeding ground for mold and mildew if not properly maintained. These microorganisms can produce unpleasant odors and pose health risks to occupants. Using anti-microbial treatments and ensuring proper drainage of condensed water can help prevent these issues. Regularly replacing the cabin air filter also aids in maintaining a clean environment around the evaporator.
Expansion Valve
The expansion valve plays a critical role in regulating the flow of refrigerant into the evaporator. Acting as a control mechanism, it ensures that the correct amount of refrigerant enters the evaporator at the right pressure and temperature. By doing so, it maximizes the efficiency of the cooling process while preventing damage to the system caused by excessive pressure.
This valve operates by sensing the temperature and pressure of the refrigerant exiting the evaporator. Based on these readings, it adjusts the opening size to allow more or less refrigerant to flow through. This dynamic adjustment ensures that the evaporator remains within its optimal operating range, providing consistent cooling regardless of external conditions.
Proper calibration of the expansion valve is essential for the system's performance. If the valve becomes clogged or malfunctions, it can disrupt the balance of the system, leading to inefficient cooling or even compressor damage. Regular inspections and cleaning can help prevent such issues. In some cases, replacing the valve may be necessary if it cannot be repaired.
Orifice Tube
In some vehicles, the orifice tube serves a similar purpose to the expansion valve. It controls the flow of refrigerant into the evaporator by creating a pressure drop between the high-pressure side and the low-pressure side of the system. Unlike the expansion valve, the orifice tube does not actively adjust based on temperature or pressure changes; instead, it maintains a fixed restriction.
The orifice tube is typically located in the inlet tube of the evaporator core. Its design allows for a precise amount of refrigerant to pass through, ensuring that the evaporator operates efficiently. However, since it lacks the adaptive capabilities of an expansion valve, vehicles equipped with orifice tubes may require periodic adjustments to maintain optimal performance.
Maintaining the orifice tube involves checking for blockages caused by debris or contaminants. A clogged orifice tube can severely restrict refrigerant flow, leading to poor cooling performance. Replacing the tube if necessary is relatively straightforward but should be done carefully to avoid introducing air or moisture into the system.
Accumulator
The accumulator is a component found in systems utilizing an orifice tube rather than an expansion valve. Its primary function is to store excess refrigerant and remove moisture and debris from the system. By filtering out contaminants, the accumulator helps protect the compressor and other sensitive components from damage.
Inside the accumulator, a desiccant material absorbs any moisture present in the refrigerant. Since water can react with refrigerants to form corrosive acids, removing it is crucial for preserving the integrity of the system. The accumulator also acts as a reservoir, holding surplus refrigerant until it is needed by the evaporator.
Regular replacement of the accumulator is recommended, especially after major repairs or if the system has been exposed to moisture. Over time, the desiccant loses its effectiveness, and the accumulator itself can become clogged with debris. Ensuring that the accumulator is functioning correctly can prolong the life of the entire air conditioning system.
Receiver/Drier
For systems equipped with an expansion valve, the receiver/drier performs functions similar to those of the accumulator. It stores excess refrigerant and filters out contaminants, protecting the system from damage. The receiver/drier also contains desiccant to absorb moisture, preventing the formation of harmful acids.
Unlike the accumulator, the receiver/drier is positioned on the high-pressure side of the system, between the condenser and the expansion valve. Its location allows it to monitor the refrigerant's condition before it enters the evaporator. Regular inspection and replacement of the receiver/drier are necessary to maintain system reliability.
Refrigerant
The refrigerant is the substance that facilitates the heat exchange process throughout the air conditioning system. Modern vehicles commonly use R-134a or newer alternatives like R-1234yf, which are environmentally friendly and efficient. The refrigerant undergoes phase changes—alternating between liquid and gas states—as it travels through the system, absorbing and releasing heat along the way.
Ensuring that the refrigerant level is appropriate is key to maintaining the system's performance. Low refrigerant levels can result in insufficient cooling, while overcharging the system can cause excessive pressure and potential damage. Regular checks and recharges, performed by qualified technicians, are recommended to keep the system operating at peak efficiency.
Hoses
The hoses connect the various components of the air conditioning system, allowing the refrigerant to flow smoothly between them. These hoses are made from materials designed to withstand the pressures and temperatures associated with the system. Over time, however, they can degrade due to exposure to heat, ozone, and other environmental factors.
Inspecting the hoses for signs of wear, such as cracks or bulges, is an important part of routine maintenance. Replacing damaged hoses promptly can prevent leaks and ensure the system remains sealed. Using high-quality replacement parts can enhance durability and extend the lifespan of the hoses.
Seals
Seals are used throughout the air conditioning system to maintain a tight seal between components, preventing refrigerant leaks. These seals are subject to constant stress due to the high pressures and temperature fluctuations within the system. Over time, they can dry out, crack, or become brittle, leading to leaks.
Regularly checking the seals for signs of deterioration is essential for maintaining system integrity. Applying a compatible sealant or lubricant can help preserve their flexibility and longevity. If leaks are detected, identifying and replacing the affected seals quickly can prevent further damage to the system.
Electrical Components
Finally, the electrical components of the air conditioning system include sensors, relays, switches, and control modules that manage the operation of the system. These components ensure that the compressor, fans, and other parts function correctly and respond appropriately to driver inputs.
Troubleshooting electrical issues requires a thorough understanding of the system's wiring and circuitry. Faulty connections, blown fuses, or malfunctioning sensors can all disrupt the system's performance. Using diagnostic tools to pinpoint the source of the problem can save time and effort during repairs.
Detailed Checklist for Maintaining Your Car's AC System
To ensure your car's air conditioning system remains in top condition, follow this detailed checklist:
1. Regular Inspections
- Check the compressor: Listen for unusual noises when the compressor engages. Look for signs of oil leaks around the mounting points.
- Inspect the condenser: Clean the fins regularly to remove dirt and debris. Ensure there are no visible signs of damage or corrosion.
- Examine the evaporator: Pay attention to any musty odors emanating from the vents, which could indicate mold growth. Schedule professional cleaning if necessary.
2. Monitor Refrigerant Levels
- Use a refrigerant gauge: Measure the pressure in the system to determine if the refrigerant level is within the manufacturer's specifications.
- Recharge as needed: Add refrigerant using a compatible recharge kit. Follow the instructions carefully to avoid overcharging.
3. Maintain Hoses and Seals
- Inspect for leaks: Look for oily residues on the exterior of the hoses and seals. Replace any components showing signs of wear or damage.
- Apply sealant: Use a recommended sealant product to reinforce existing seals and prevent future leaks.
4. Service Electrical Components
- Test sensors and switches: Verify that all sensors and switches are functioning correctly. Replace faulty components immediately.
- Check wiring and connections: Ensure all electrical connections are secure and free from corrosion. Repair or replace damaged wires as needed.
By following this checklist diligently, you can enjoy a reliable and efficient air conditioning system year-round. Remember, regular maintenance not only improves performance but also extends the life of your car's AC system.
Deja una respuesta